
Salesforce Integration Architect Interview Questions

Table of Contents
- Main components
- SOAP and REST APIs in Salesforce.
- Salesforce Integration Architect
- Salesforce Outbound and Inbound Messaging
- Salesforce integration patterns
- What is an External ID?
- Salesforce integration design
- Data validation in Salesforce integrations
- Design a disaster recovery plan
When preparing for a Salesforce Integration Architect role, it’s crucial to thoroughly understand the core concepts and challenges that come with integrating Salesforce into a broader enterprise ecosystem. The following set of questions and answers is designed to provide in-depth insights into the key areas of expertise required for such a role, ranging from API management and data validation to multi-cloud integrations and compliance with data protection regulations.
By mastering these topics, you’ll not only demonstrate your technical proficiency but also showcase your ability to design, implement, and manage complex integrations that align with business goals and ensure the integrity and security of data.
These questions are more than just a study guide; they offer a framework for thinking critically about the responsibilities and challenges of a Salesforce Integration Architect. By practicing these answers, you’ll be able to articulate your experience and approach in a way that resonates with potential employers.
Whether you’re discussing your experience with integration patterns, your strategies for handling API limits, or your approach to disaster recovery, these responses will help you convey your ability to contribute effectively to any organization’s Salesforce integration initiatives.
This preparation will position you as a strong candidate who is not only technically adept but also strategic and forward-thinking in your approach to Salesforce integrations.
Are you looking to upgrade your career in Salesforce?
Yes, we have the perfect solution for you with our comprehensive Salesforce training in Hyderabad. This course is designed to cover everything you need to know, from admin and developer roles to LWC modules, ensuring you become job-ready. Enroll for Free Demo today!
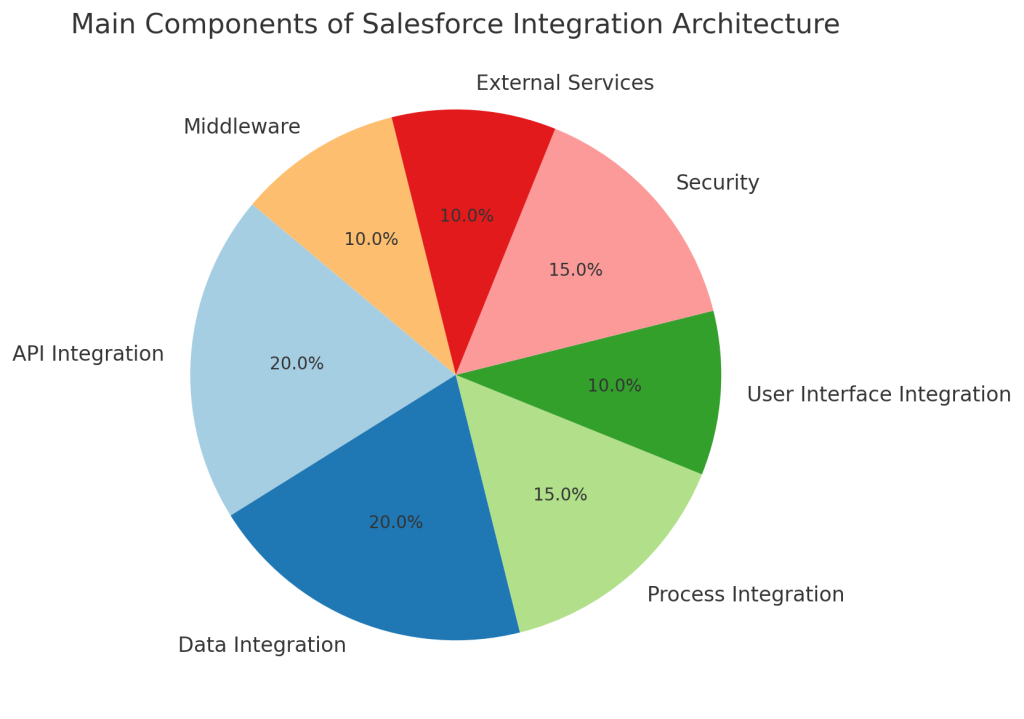
1. What are the main components of the Salesforce integration architecture?
As a Salesforce Integration Architect, I focus on several critical components that form the foundation of our integration architecture. The first and foremost are Salesforce APIs, such as REST, SOAP, Bulk API, and Streaming API, which facilitate communication between Salesforce and other systems. These APIs serve as the primary method for sending and receiving data.
In addition to APIs, middleware platforms, like an Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) or Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS), are essential for orchestrating complex integrations. Middleware acts as a bridge, enabling seamless data flow between Salesforce and external applications. We also utilize data mapping and transformation tools to ensure that data is correctly interpreted and converted as it moves between systems.
Finally, robust monitoring, logging, and error-handling frameworks are crucial for maintaining the performance and reliability of our integrations. By leveraging these components, I can design and implement integrations that meet the organization’s needs while ensuring data integrity and system efficiency.
These Salesforce interview questions are your ultimate toolkit for landing your next job opportunity. Mastering them is essential for anyone striving to excel as a Salesforce Admin or Developer. They encompass all the critical topics you’ll encounter, ensuring you’re thoroughly prepared. From mastering technical skills to understanding real-world applications, you’ll build the confidence needed to succeed. Begin your practice now and unleash your potential in the Salesforce industry. Always remember, thorough preparation is the foundation of your success!
2. What Salesforce API would you use to bulk load millions of records?
When it comes to bulk loading millions of records into Salesforce, I always opt for the Salesforce Bulk API 2.0. This API is specifically designed for handling large data sets efficiently. What I appreciate most about the Bulk API is its asynchronous processing capability, which allows me to submit data in batches without waiting for each operation to complete before proceeding with the next. This significantly speeds up the process, especially when dealing with massive amounts of data.
The Bulk API can handle up to 100,000 records per batch, making it ideal for large-scale data imports. Its ability to work with CSV files for input adds to its flexibility, allowing me to insert, update, upsert, or delete records as needed. Additionally, I find the job and batch status tracking features invaluable for monitoring the progress and ensuring that the data load is proceeding as expected. By using the Bulk API, I can efficiently manage high-volume data tasks while minimizing the risk of errors and ensuring that the data is accurately processed within Salesforce.
Join the demo of this Salesforce course for free – it’s a career-changing, job-oriented certification course that will equip you with the skills you need to succeed.
Here’s a small code snippet that demonstrates how to use Salesforce’s Bulk API to insert a large number of records into the Account object.
Example: Using Salesforce Bulk API to Insert Records
public class BulkApiExample {
public void insertBulkRecords() {
// Step 1: Create a job to insert records
JobInfo job = new JobInfo();
job.setObject('Account'); // Specify the object
job.setOperation('insert'); // Specify the operation (insert, update, upsert, etc.)
job.setContentType('CSV'); // Data format
job.setConcurrencyMode('Parallel'); // Mode: Parallel or Serial
// Step 2: Create the job
job = [SELECT Id, Object, Operation, ContentType, State FROM JobInfo WHERE Id = :job.Id];
// Step 3: Prepare a batch of records in CSV format
String csvData = 'Name,Industry\n' +
'Account 1,Technology\n' +
'Account 2,Healthcare\n' +
'Account 3,Finance';
// Step 4: Add the batch to the job
BatchInfo batch = new BatchInfo();
batch.setJobId(job.Id);
batch.setCsvData(csvData);
// Step 5: Close the job to start processing
job.setState('Closed');
// Step 6: Monitor the job status (optional, for tracking)
System.debug('Bulk API job created with ID: ' + job.Id);
}
}Explanation:
- Job Creation: The
JobInfoobject is used to create a job specifying the object (Account), the operation (insert), and the content type (CSV). - CSV Data Preparation: A simple CSV string is created to represent the data you want to load into Salesforce.
- Batch Submission: The
BatchInfoobject is used to submit the CSV data to the Bulk API job. - Job Execution: The job is then closed to signal that it is ready to be processed by Salesforce.
- Monitoring: You can monitor the status of the job, though this step is optional in this example.
This code snippet shows a basic example of how you might use the Bulk API in Salesforce to handle large volumes of data efficiently.
See also: Salesforce Admin Exam Guide 2024
3. Describe your approach to Salesforce integration testing.
In my approach to Salesforce integration testing, I prioritize thoroughness and attention to detail. The first step involves defining test scenarios that align with the business requirements and use cases. These scenarios guide the entire testing process, ensuring that we cover all critical aspects of the integration. I then conduct tests in a sandbox environment, which mirrors the production setup as closely as possible. This allows me to test with production-like data volumes and configurations, ensuring that any issues encountered in testing are likely to reflect those in a live environment.
Unit testing is another essential part of my approach, where I test individual components like mappings, conversions, and connectivity. This step helps in identifying and resolving issues at a granular level before moving on to more complex scenarios. Once the unit tests are successful, I perform end-to-end integration tests to validate the complete data flow across systems. During this phase, I pay close attention to the accuracy of data mappings, error handling, and fault tolerance.
To ensure robustness, I also run performance and load tests, pushing the API and system limits to identify potential bottlenecks. Automated regression tests are another critical component, helping to quickly identify any issues that might have been introduced with new changes. Lastly, I involve actual business users in User Acceptance Testing (UAT), ensuring that the integration meets their expectations and requirements. This comprehensive approach allows me to deliver high-quality, reliable integrations.
See also: Mastering Email Address Validation in Salesforce
Testing a REST API Callout
Let’s assume you have an integration where Salesforce makes a REST API callout to an external system to fetch account details.
1. Integration Class
public class AccountIntegration {
public static Account fetchAccountDetails(String accountId) {
// Prepare the HTTP request
HttpRequest req = new HttpRequest();
req.setEndpoint('https://externalapi.com/accounts/' + accountId);
req.setMethod('GET');
req.setHeader('Authorization', 'Bearer ' + getAccessToken());
// Send the HTTP request and receive the response
Http http = new Http();
HttpResponse res = http.send(req);
// Handle the response
if (res.getStatusCode() == 200) {
// Parse the response and return the account details
Account acc = (Account)JSON.deserialize(res.getBody(), Account.class);
return acc;
} else {
// Handle errors
throw new CustomException('Error fetching account details: ' + res.getStatusCode());
}
}
private static String getAccessToken() {
// Logic to retrieve OAuth access token
return 'mock_access_token';
}
}
2. Test Class Using Mocking
@IsTest
public class AccountIntegrationTest {
// Mock class to simulate the API response
public class MockHttpResponseGenerator implements HttpCalloutMock {
public HttpResponse respond(HttpRequest req) {
HttpResponse res = new HttpResponse();
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'application/json');
res.setBody('{"Id":"001xx000003DGbEAAW","Name":"Test Account","Industry":"Technology"}');
res.setStatusCode(200);
return res;
}
}
@IsTest
static void testFetchAccountDetails() {
// Set the mock class
Test.setMock(HttpCalloutMock.class, new MockHttpResponseGenerator());
// Call the method being tested
Account acc = AccountIntegration.fetchAccountDetails('001xx000003DGbEAAW');
// Verify the results
System.assertEquals('Test Account', acc.Name);
System.assertEquals('Technology', acc.Industry);
}
@IsTest
static void testFetchAccountDetailsWithError() {
// Mock class to simulate an error response
public class MockHttpErrorResponseGenerator implements HttpCalloutMock {
public HttpResponse respond(HttpRequest req) {
HttpResponse res = new HttpResponse();
res.setStatusCode(500);
res.setBody('{"error":"Internal Server Error"}');
return res;
}
}
// Set the mock error response
Test.setMock(HttpCalloutMock.class, new MockHttpErrorResponseGenerator());
// Expect an exception to be thrown
try {
AccountIntegration.fetchAccountDetails('001xx000003DGbEAAW');
System.assert(false, 'Expected an exception to be thrown');
} catch (CustomException e) {
System.assertEquals('Error fetching account details: 500', e.getMessage());
}
}
}
Explanation:
- Integration Class (
AccountIntegration):- This class contains the method
fetchAccountDetails, which makes a REST API call to an external system to retrieve account details. - The response is parsed, and if successful, an
Accountobject is returned. Otherwise, an exception is thrown.
- This class contains the method
- Test Class (
AccountIntegrationTest):- The test class uses the
HttpCalloutMockinterface to simulate HTTP responses from the external system. - Positive Test (
testFetchAccountDetails): This test simulates a successful API response and verifies that the returned account data matches the expected values. - Negative Test (
testFetchAccountDetailsWithError): This test simulates an error response (HTTP 500) and verifies that the appropriate exception is thrown with the correct message.
- The test class uses the
- Mocking:
- The
MockHttpResponseGeneratorandMockHttpErrorResponseGeneratorclasses simulate different scenarios, allowing you to test how your code handles various responses from the external system.
- The
Read more: Roles and Profiles in Salesforce
4. How do you handle versioning and backward compatibility in Salesforce integrations?
Handling versioning and backward compatibility in Salesforce integrations is crucial for maintaining stable and reliable integrations, especially in a dynamic environment where Salesforce releases new API versions multiple times a year. My approach starts with careful planning and documentation. For each integration, I explicitly reference the API version in the endpoint URLs and WSDL imports, ensuring that the integration continues to function correctly even as Salesforce evolves.
Before Salesforce rolls out a new release, I perform regression testing in a sandbox environment that mimics the production setup. This allows me to identify any potential issues with the new API version and address them proactively. I also maintain separate classes and configurations for different API versions, which helps in managing backward compatibility. This way, if an older system or third-party tool requires a previous version, I can continue to support it without disrupting the overall integration.
In cases where breaking changes are inevitable, I collaborate closely with the release management team to plan and execute a smooth transition. This includes updating integration documentation, communicating changes to stakeholders, and ensuring that all related systems are prepared for the update. By staying ahead of versioning challenges, I can ensure that our integrations remain stable and continue to meet the business’s needs.
5. Explain the difference between SOAP and REST APIs in Salesforce.
SOAP and REST APIs in Salesforce serve as the backbone for integrating various systems, but they differ significantly in their structure and use cases. SOAP, or Simple Object Access Protocol, is a more traditional web service protocol that uses XML for its message format. One of the key advantages of SOAP is its strict standards and built-in security features, making it ideal for complex enterprise integrations where data integrity and security are paramount. SOAP APIs also come with a WSDL (Web Services Description Language) contract, which clearly defines the available operations and their inputs/outputs, providing a robust framework for developers to work within.
On the other hand, REST, or Representational State Transfer, offers a more lightweight and flexible approach. REST APIs use standard HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) and typically work with JSON payloads, which are easier to work with in modern web and mobile applications. REST is often preferred for its simplicity and ease of use, particularly in scenarios where rapid development and deployment are required. However, it’s important to note that REST might not always offer the same level of security and transaction support as SOAP, which can be a consideration in highly regulated environments. Both APIs have their strengths, and choosing the right one depends on the specific needs of the integration.
Code Examples
SOAP API Example
Let’s say we need to make a SOAP API call from Salesforce to an external service. Here’s a simple example:
public class SoapApiExample {
public void callSoapApi() {
// Define the endpoint for the SOAP API
String endpoint = 'https://www.example.com/soap-service';
// Construct the SOAP request XML
String requestXml = '<soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" ' +
'xmlns:web="http://www.example.com/webservice">' +
'<soapenv:Header/>' +
'<soapenv:Body>' +
'<web:GetAccountDetails>' +
'<web:accountId>001xx000003DGbEAAW</web:accountId>' +
'</web:GetAccountDetails>' +
'</soapenv:Body>' +
'</soapenv:Envelope>';
// Set up the HTTP request
HttpRequest req = new HttpRequest();
req.setEndpoint(endpoint);
req.setMethod('POST');
req.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/xml');
req.setHeader('SOAPAction', 'GetAccountDetails');
req.setBody(requestXml);
// Make the callout and handle the response
Http http = new Http();
HttpResponse res = http.send(req);
if (res.getStatusCode() == 200) {
System.debug('SOAP Response: ' + res.getBody());
} else {
System.debug('SOAP call failed: ' + res.getStatusCode() + ' ' + res.getStatus());
}
}
}
Explanation:
- A SOAP envelope is constructed in XML format, and the request is sent via a
POSTHTTP method. - The
SOAPActionheader is used to specify the action being requested. - The response is parsed and handled appropriately.
REST API Example
Let’s now consider a REST API call from Salesforce to fetch account details from an external service.
public class RestApiExample {
public void callRestApi() {
// Define the endpoint for the REST API
String endpoint = 'https://www.example.com/api/accounts/001xx000003DGbEAAW';
// Set up the HTTP request
HttpRequest req = new HttpRequest();
req.setEndpoint(endpoint);
req.setMethod('GET');
req.setHeader('Authorization', 'Bearer ' + getAccessToken());
req.setHeader('Accept', 'application/json');
// Make the callout and handle the response
Http http = new Http();
HttpResponse res = http.send(req);
if (res.getStatusCode() == 200) {
System.debug('REST Response: ' + res.getBody());
// Parse JSON response
Map<String, Object> jsonResponse = (Map<String, Object>)JSON.deserializeUntyped(res.getBody());
System.debug('Account Name: ' + jsonResponse.get('name'));
} else {
System.debug('REST call failed: ' + res.getStatusCode() + ' ' + res.getStatus());
}
}
private static String getAccessToken() {
// Logic to retrieve OAuth access token
return 'mock_access_token';
}
}
Explanation:
- The REST API call is made using the
GETHTTP method. - JSON is the preferred format, and the response is parsed using Salesforce’s JSON parser.
- Authorization is handled via an OAuth token.
Read more: Triggers in Salesforce interview Questions
6. How do you monitor Salesforce API usage and limits?
Monitoring Salesforce API usage and limits is essential to ensure that our integrations run smoothly and do not hit any roadblocks. Salesforce enforces daily API limits to maintain system performance and fairness among users. To stay within these limits, I regularly review the API usage metrics available in Salesforce Setup under System Overview. This section provides a near real-time view of how many API calls have been used out of the daily allocation. Additionally, I use API Usage reports to gain insights into the number of requests, the average processing time, and the specific clients generating the most calls.
For more detailed monitoring, I leverage the REST API Limits resource, which provides the current status of API limits programmatically. This is particularly useful for integrating proactive checks within our middleware or custom applications, enabling us to trigger alerts or take corrective actions when usage approaches critical thresholds. I also ensure that our Apex code adheres to best practices by using the Limits Apex methods, which help track governor limits and avoid excessive API consumption during processing. By staying vigilant and using these monitoring tools, I can prevent disruptions and maintain the efficiency and reliability of our Salesforce integrations.
7. What are some techniques to optimize Salesforce integration performance?
Optimizing Salesforce integration performance is a priority for me, especially when dealing with large data volumes or complex integrations. One of the first techniques I employ is the use of the Salesforce Bulk API or Platform Events API for handling large datasets. These APIs are designed to process records in batches, which significantly reduces processing time and system load compared to traditional SOAP or REST APIs. By leveraging these APIs, I can ensure that even massive data operations are completed efficiently without overwhelming the system.
Another key strategy is optimizing SOQL queries. I always strive to make queries as selective as possible by using indexed fields and applying filters that limit the amount of data retrieved. This not only speeds up the queries but also reduces the overall load on the database. I also pay close attention to avoiding DML operations within loops, instead using collections and bulk methods to process data in batches. This approach minimizes the number of transactions and helps in staying within Salesforce’s governor limits.
Additionally, I work on optimizing middleware and external systems by enabling caching, indexing, and parallel processing where applicable. Monitoring API response times and adjusting batch sizes, pagination, and other parameters also help in maintaining optimal performance. By combining these techniques, I can ensure that our Salesforce integrations are both efficient and scalable, even under heavy loads.
public class IntegrationOptimizationExample {
// Use Queueable Apex for Asynchronous Processing
public void processLargeDataSet(List<Account> accounts) {
// Submit a job to process records asynchronously
System.enqueueJob(new AccountProcessingJob(accounts));
}
// Queueable Apex to process records in batches
public class AccountProcessingJob implements Queueable, Database.AllowsCallouts {
private List<Account> accounts;
public AccountProcessingJob(List<Account> accounts) {
this.accounts = accounts;
}
public void execute(QueueableContext context) {
// Use Bulk API for large data insert
if (!accounts.isEmpty()) {
insert accounts; // Bulk insert to optimize DML operations
}
}
}
// Efficient SOQL Query
public List<Account> getAccountData(String industry) {
// Query only necessary fields to reduce load
List<Account> accountList = [SELECT Id, Name FROM Account WHERE Industry = :industry LIMIT 200];
return accountList;
}
// Caching frequently accessed data
public String getCachedIndustrySetting() {
// Use custom settings or platform cache for repeated data retrieval
String industry = MyCustomSetting__c.getInstance('DefaultIndustry').Industry__c;
return industry;
}
}
The code example demonstrates several key techniques to optimize Salesforce integration performance, especially when dealing with large data volumes and complex integration scenarios.
Asynchronous Processing with Queueable Apex
The first technique involves the use of Queueable Apex for asynchronous processing. In the processLargeDataSet method, the code submits a job to handle large datasets asynchronously by using the System.enqueueJob method. This technique improves the user experience and system performance by offloading long-running operations from the main thread, allowing users to continue their work without experiencing delays. The Queueable Apex job (AccountProcessingJob) is responsible for processing the records in the background. By handling tasks asynchronously, the system can better manage resources and reduce the likelihood of hitting governor limits.
Bulk API for Large Data Operations
Within the AccountProcessingJob class, the code utilizes Salesforce’s Bulk API to handle large data operations efficiently. Instead of processing records one at a time, the example shows how to perform a bulk insert operation (insert accounts). The Bulk API is particularly effective when dealing with large volumes of data, as it reduces the number of DML operations required and optimizes the process by grouping multiple records into a single batch. This not only speeds up the integration process but also helps to stay within Salesforce’s governor limits, which can be a concern when dealing with massive datasets.
See also: Salesforce Admin Interview Questions
Efficient SOQL Queries
The third technique focuses on optimizing SOQL queries by selecting only the necessary fields. In the getAccountData method, the SOQL query retrieves only the Id and Name fields from the Account object, based on a specified industry. By limiting the number of fields returned by the query, the system reduces the load on the database and minimizes the amount of data that needs to be processed and transferred. This approach enhances performance by making queries faster and more efficient, especially when dealing with large datasets.
Caching Frequently Accessed Data
Lastly, the code highlights the importance of caching frequently accessed data to improve performance. The getCachedIndustrySetting method retrieves a commonly used industry setting from custom settings or platform cache, rather than querying the database repeatedly. Caching is a powerful technique for reducing the number of database queries, which can significantly enhance performance in scenarios where the same data is accessed multiple times. By storing this data in a readily accessible cache, the system can quickly retrieve it without incurring the overhead of a database call.
In summary, the code example illustrates how to optimize Salesforce integration performance through asynchronous processing with Queueable Apex, efficient use of the Bulk API for large data operations, optimized SOQL queries, and caching of frequently accessed data. These techniques collectively ensure that the integration processes are robust, scalable, and efficient, providing a better experience for users and reducing the load on system resources.
8. What is the role of a Salesforce Integration Architect?
As a Salesforce Integration Architect, my role is to design and implement seamless integrations between Salesforce and other enterprise systems. This involves understanding the unique business requirements of the organization and translating them into technical solutions that facilitate data flow between systems like ERP, marketing automation platforms, and legacy databases. I work closely with stakeholders across departments to map data flows, choose the appropriate integration patterns, and select the best tools and technologies for the job.
In addition to designing the architecture, I am responsible for ensuring that the integrations are robust, secure, and scalable. This includes managing data integrity, optimizing performance, and implementing monitoring and error-handling mechanisms. I also oversee the entire lifecycle of the integration, from development and testing to deployment and ongoing maintenance. My goal is to create integrations that not only meet current business needs but are also adaptable to future requirements, ensuring that the organization can continue to grow and evolve without being held back by technical limitations.
9. Describe your experience with Salesforce integration tools and platforms.
Over the years, I’ve had the opportunity to work with a variety of Salesforce integration tools and platforms, each with its unique strengths and use cases. My experience includes hands-on work with industry-leading tools like Mulesoft, Dell Boomi, Jitterbit, SnapLogic, and Informatica Cloud. These platforms have allowed me to solve a wide range of integration challenges, from simple point-to-point integrations to more complex, enterprise-level data orchestration across multiple systems.
For instance, with Mulesoft, I’ve designed API-led connectivity solutions that enable modular, reusable integrations, which are crucial for maintaining agility in a fast-paced business environment. Dell Boomi has been particularly useful for cloud-to-cloud integrations, where its visual interface and pre-built connectors have sped up development time. On the other hand, when dealing with on-premise legacy systems, Jitterbit’s hybrid integration capabilities have proven invaluable. Throughout these experiences, I’ve developed a deep understanding of how to configure connections, manage data mappings and transformations, and deploy and monitor integration processes. My expertise with these tools allows me to tailor solutions to the specific needs of each project, ensuring efficient and reliable integrations.
10. How do you choose between real-time and batch data integration?
Choosing between real-time and batch data integration is a critical decision that depends on several factors. Real-time integration is essential when immediate data consistency is required across systems. For example, if I’m working on syncing active sales opportunities or support cases between Salesforce and an ERP system, real-time integration ensures that the data is always up-to-date, which is crucial for operational efficiency and decision-making. In these cases, I would opt for real-time methods such as Salesforce’s Streaming API or Platform Events.
On the other hand, batch-based integration is more appropriate for scenarios where data doesn’t need to be updated instantaneously. This is often the case with large data sets that are processed at specific intervals, such as end-of-day financial transactions or historical data migrations. Batch processing allows for more efficient handling of large volumes of data without overloading the system. Factors like the frequency of data changes, the size of the data, and the performance capabilities of the systems involved all influence my decision. By carefully considering these factors, I can select the most appropriate integration method to balance performance, efficiency, and business needs.
Real-Time Data Integration
Use Case: Real-time data integration is ideal when you need instant data synchronization between systems, such as updating a customer record in Salesforce immediately after a transaction occurs in another system. It ensures that the data is always up-to-date, which is crucial for time-sensitive processes like order processing or customer support.
Example: You can implement real-time integration using Salesforce’s Platform Events, which allow you to publish and subscribe to event messages that are instantly processed.
Code Example:
// Define a Platform Event to handle real-time data integration
public class OrderProcessingEvent {
@InvocableMethod
public static void handleOrderEvent(List<PlatformEvent__e> eventList) {
for (PlatformEvent__e eventRecord : eventList) {
// Process the event, for example, create or update a record in Salesforce
Order__c newOrder = new Order__c();
newOrder.OrderID__c = eventRecord.OrderID__c;
newOrder.CustomerID__c = eventRecord.CustomerID__c;
newOrder.Status__c = eventRecord.Status__c;
insert newOrder;
}
}
}In this example, when an order is processed in an external system, a platform event is triggered, and Salesforce listens for this event to create or update an order record in real-time.
See more: Salesforce JavaScript Developer Interview Questions
Batch Data Integration
Use Case: Batch data integration is more suitable for scenarios where data can be processed in bulk at scheduled intervals, such as nightly updates of large datasets. It’s useful when dealing with high volumes of data that do not need immediate synchronization, which helps to reduce the load on the system during peak times.
Example: Salesforce Batch Apex is commonly used for batch data integration. It processes large volumes of records asynchronously, breaking them into manageable chunks.
Code Example:
global class BatchOrderUpdate implements Database.Batchable<SObject> {
global Database.QueryLocator start(Database.BatchableContext BC) {
// Query for orders that need to be updated
return Database.getQueryLocator([SELECT Id, Status__c FROM Order__c WHERE Status__c = 'Pending']);
}
global void execute(Database.BatchableContext BC, List<SObject> scope) {
// Process each batch of orders
for (Order__c order : (List<Order__c>) scope) {
// Update the order status to 'Processed'
order.Status__c = 'Processed';
}
update scope;
}
global void finish(Database.BatchableContext BC) {
// Final actions after all batches are processed
System.debug('Batch processing complete.');
}
}In this example, the batch job queries all orders with a ‘Pending’ status and updates them to ‘Processed’ in batches. This approach is efficient for handling large data sets without overloading the system.
Choosing Between the Two
- Real-Time Integration: Choose this when data accuracy and immediacy are crucial, and when data changes need to be reflected instantly across systems. However, be mindful of the impact on system performance with frequent data synchronization.
- Batch Integration: Opt for batch processing when dealing with large data volumes that do not require immediate synchronization. This method is more scalable and can be scheduled during off-peak hours to minimize system load.
11. Explain the difference between Salesforce Outbound and Inbound Messaging.
The difference between Salesforce Outbound and Inbound Messaging lies in the direction and purpose of the data flow. Outbound Messaging is a push mechanism where Salesforce sends a SOAP message with an XML payload to an external system when certain criteria are met in a record. This is often used to trigger downstream processes or updates in other systems, making it ideal for situations where an external system needs to be notified immediately after a specific event occurs in Salesforce, such as when a new lead is created or an opportunity is closed.
Inbound Messaging, on the other hand, is a pull mechanism. Here, an external system sends SOAP or REST requests to Salesforce to create, update, or retrieve records. This is typically used when an external system needs to send data into Salesforce, like syncing customer records from a third-party CRM or updating inventory levels from an ERP system. While both methods are essential for different integration scenarios, the choice between them depends on whether Salesforce needs to push data out or if it needs to receive and process incoming data from another system.
See also: Accenture LWC Interview Questions
12. How do you troubleshoot and debug Salesforce integration issues?
When troubleshooting and debugging Salesforce integration issues, I follow a systematic approach to identify and resolve the root cause effectively. The first step is to review the integration logs, either in Salesforce or in the middleware platform, to check for any error messages or exceptions. These logs provide valuable information about where the failure occurred, whether it’s in the data payload, the connectivity, or the authentication process.
Next, I analyze the API request and response payloads, looking for any discrepancies or mismatches in the data. Tools like Postman or SOAP UI are extremely helpful for this, allowing me to test the API calls directly and inspect the responses. If the issue involves Apex callouts, I dive into the Salesforce debug logs to trace the exact point of failure. In cases where the problem might be related to connectivity or permissions, I verify endpoint URLs, authentication credentials, and user permissions to ensure everything is configured correctly.
Additionally, I enable detailed logging and tracing in the middleware to capture more granular details, which can often reveal hidden issues. If necessary, I reproduce the issue in a sandbox environment to isolate the problem without affecting the production environment. This methodical approach allows me to pinpoint the cause of the issue and implement the necessary fixes, ensuring that the integration runs smoothly.
See also: Salesforce SOQL and SOSL Interview Questions
13. Describe your experience with Salesforce integration patterns.
In my career as a Salesforce Integration Architect, I’ve worked extensively with various integration patterns, each suited to different business needs and technical requirements. One of the most common patterns I’ve implemented is the Broadcast pattern, where Salesforce publishes events that are consumed by multiple subscribers. This pattern is particularly useful in scenarios where data needs to be shared across several systems simultaneously, such as sending customer updates to both a CRM and a marketing automation platform.
I’ve also worked on Aggregation patterns, where data from multiple sources is combined into Salesforce. This is often used in reporting and analytics scenarios where data from different systems, such as ERP and e-commerce platforms, needs to be centralized for better visibility. Another pattern I frequently encounter is Bi-directional Sync, which involves synchronizing data between Salesforce and another system. This pattern is crucial for maintaining consistency across systems, ensuring that changes in one system are reflected in the other.
Moreover, I’ve implemented Data Virtualization, where data is abstracted in middleware views without physically copying it into Salesforce. This is particularly beneficial in reducing data storage costs and improving performance by avoiding unnecessary data replication. Throughout my experience, I’ve learned to analyze each integration scenario carefully and select the most appropriate pattern to meet the specific requirements, ensuring efficient and scalable solutions.
Read more: TCS Salesforce Interview Questions
14. What security considerations are important for Salesforce integrations?
Security is a top priority in any Salesforce integration, and I take several key considerations into account to ensure that data is protected at every step. The first aspect I focus on is authentication, where I prefer using OAuth 2.0 for secure API access. OAuth not only provides strong authentication but also allows for fine-grained control over what each integration can do within Salesforce, reducing the risk of unauthorized actions.
Encryption is another critical factor. I ensure that all data in transit is encrypted using SSL/TLS, which prevents data interception during transmission. For data at rest, I rely on Salesforce’s built-in encryption features to protect sensitive information. Access control is also vital, so I make sure that API access is restricted through Salesforce Connected Apps, Profiles, and Permission Sets, applying the principle of least privilege to minimize potential exposure.
Moreover, I implement logging and monitoring to detect any unusual activity or potential security breaches. This includes setting up alerts for abnormal API usage patterns and conducting regular security audits and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities. By combining these security measures, I can ensure that our Salesforce integrations are not only effective but also secure, safeguarding the organization’s data and compliance with regulatory standards like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS.
Read more: Salesforce Service Cloud Interview Questions
15. What is an External ID, and how is it used?
An External ID in Salesforce is a custom field that plays a crucial role in data integration and synchronization processes. It uniquely identifies a record in Salesforce based on a corresponding identifier in an external system, such as a customer ID or product code from an ERP or CRM. The primary use of an External ID is in upserting operations, where Salesforce needs to determine whether to update an existing record or insert a new one. By using an External ID, Salesforce can match incoming data to existing records without creating duplicates, which is especially useful when dealing with large data sets or multiple systems.
In addition to preventing duplicates, External IDs are also used to maintain relationships between integrated objects across systems. For example, when importing data that includes related objects, such as accounts and contacts, External IDs help ensure that the correct relationships are established within Salesforce, matching external system IDs to Salesforce record IDs. This feature not only simplifies data management but also enhances the accuracy and efficiency of integrations, making it easier to keep data consistent and up-to-date across platforms.
Example Scenario:
Let’s say you have a custom object called Customer__c in Salesforce, and you want to upsert records from an external system where the unique identifier is External_Customer_ID__c.
Apex Code Example:
// Assume we receive a list of customer records from an external system
List<Customer__c> externalCustomers = new List<Customer__c>();
// Creating a sample record to upsert
Customer__c customer1 = new Customer__c();
customer1.External_Customer_ID__c = 'EXT12345'; // External ID from the external system
customer1.Name = 'John Doe';
customer1.Email__c = 'johndoe@example.com';
externalCustomers.add(customer1);
// Perform an upsert operation using the External ID
// This will update the existing record if a match is found, or insert a new record if no match is found
try {
upsert externalCustomers Customer__c.External_Customer_ID__c;
System.debug('Upsert successful!');
} catch (DmlException e) {
System.debug('An error occurred during upsert: ' + e.getMessage());
}Explanation:
- Custom Object and External ID: The code assumes that there is a custom object
Customer__cwith a custom fieldExternal_Customer_ID__cmarked as an External ID. - Record Creation: The example creates a new
Customer__crecord with anExternal_Customer_ID__cof'EXT12345'. - Upsert Operation: The
upsertDML operation is used with theExternal_Customer_ID__cfield to ensure that Salesforce checks for an existing record with the same External ID. If it finds one, it updates that record; if it doesn’t, it creates a new one. - Error Handling: The code includes a try-catch block to handle any potential errors during the upsert operation.
16. What are some common challenges faced in Salesforce integrations?
Salesforce integrations, while powerful, come with their share of challenges that require careful planning and execution. One of the most common challenges I encounter is handling complex data mappings and transformations between different object models. Often, external systems have data structures that don’t align perfectly with Salesforce’s objects, requiring extensive data mapping and transformation to ensure that the data is correctly interpreted and processed within Salesforce. This can become particularly challenging when dealing with custom objects or highly customized Salesforce environments, where standard mappings may not be sufficient.
Another significant challenge is managing large data volumes and optimizing performance. Salesforce has strict governor limits, and when integrating with large datasets or performing high-frequency transactions, these limits can quickly become a bottleneck. Ensuring that the integration processes are optimized to handle large volumes without hitting these limits is crucial. This might involve using Bulk API for batch processing or implementing strategies like asynchronous processing to reduce the load on Salesforce. Additionally, maintaining integration logic across Salesforce releases and API versions adds another layer of complexity, requiring constant vigilance and proactive management to ensure compatibility and stability.
Read moare: Roles and Profiles in Salesforce Interview Questions
17. What are some best practices for Salesforce integration design?
When designing Salesforce integrations, I adhere to several best practices that ensure the integration is robust, scalable, and maintainable. First and foremost, I always advocate for using an API-led, modular architecture rather than point-to-point integrations. By creating reusable APIs for different layers (System, Process, and Experience), I can build a more flexible and scalable integration that can easily adapt to future changes or new requirements.
Another best practice is to leverage standard APIs and connectors wherever possible. This reduces development time, minimizes errors, and ensures that the integration is using well-supported and tested components. Additionally, I recommend using an Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) or iPaaS for centralizing integrations, which provides better orchestration, monitoring, and error handling capabilities across the entire integration landscape.
Data mapping, conversion, and validation are also critical aspects that I focus on during the design phase. Implementing proper data validation rules within Salesforce, as well as in the middleware, helps in maintaining data quality and consistency across systems. Finally, I ensure that there is comprehensive logging and error handling in place, which allows for easier troubleshooting and maintenance of the integration over time. By following these best practices, I can design integrations that not only meet current business needs but also remain resilient and scalable in the long run.
Read more: Accenture Salesforce Developer Interview Questions
18. How can you schedule Salesforce data exports to an external system?
Scheduling Salesforce data exports to an external system is a common requirement, and there are several methods I employ depending on the specific needs of the organization. One of the most straightforward approaches is to use Salesforce’s Data Export Service, which can generate weekly or monthly CSV exports of the entire organization’s data. This service is easy to set up and can automatically send the export files to a secure location for retrieval by an external system.
For more frequent or specific data exports, I often use Salesforce Scheduled Reports. These reports can be configured to run at set intervals, such as daily or weekly, and can be emailed in Excel or CSV format directly to the intended recipients. This method is particularly useful for generating regular updates on specific datasets, like sales performance or customer activity.
If the requirements are more complex, such as needing real-time or near real-time data synchronization, I might develop a custom Apex batch job that queries the necessary records and invokes an API callout to push the data to an external system on a scheduled basis. Alternatively, middleware tools like Mulesoft or Dell Boomi can be configured to pull data from Salesforce at regular intervals and transfer it to the target system. These tools offer advanced scheduling, transformation, and monitoring capabilities, making them ideal for more sophisticated integration scenarios.
Read more: Salesforce Experience Cloud Interview Questions
19. How do you handle data validation in Salesforce integrations?
Data validation is a critical aspect of any Salesforce integration, as it ensures that the data entering Salesforce meets the required quality and consistency standards. My approach to data validation begins with defining strict validation rules within Salesforce itself. These rules can check for field formats, ranges, and required values, ensuring that only valid data is processed and stored. For instance, I might create a validation rule to ensure that email addresses follow a specific format or that certain fields cannot be left blank when records are created or updated.
In addition to Salesforce’s native validation, I implement data type and constraint checks within the middleware or ETL tools that handle the data integration. This involves defining and enforcing data mappings, conversions, and transformations to ensure that the data is correctly interpreted and matches the expected format before it reaches Salesforce. Furthermore, I handle and log any validation errors that occur during the integration process, alerting administrators or sending error responses back to the source systems for correction. By combining these approaches, I can maintain high data quality and prevent issues related to incorrect or inconsistent data from disrupting business processes.
20. Compare API-led connectivity vs point-to-point integration approaches.
API-led connectivity and point-to-point integration represent two distinct approaches to system integration, each with its own set of advantages and challenges. In my experience, API-led connectivity offers a more structured and scalable solution, particularly in complex enterprise environments. With API-led connectivity, integrations are built using a layered approach, where reusable APIs are created for specific functions, such as unlocking data from systems (System APIs), composing data into business processes (Process APIs), and delivering the data through various channels (Experience APIs). This modular design promotes reuse, agility, and the ability to quickly adapt to changing business needs without disrupting existing integrations.
On the other hand, point-to-point integration is simpler and can be quicker to implement for straightforward, one-off connections between two systems. However, as the number of integrations grows, point-to-point connections can become difficult to manage, leading to a web of dependencies that are hard to maintain and scale. Each additional connection requires custom logic, making the system fragile and challenging to update. In contrast, API-led connectivity’s reusable components reduce redundancy, simplify maintenance, and provide a more future-proof architecture. While point-to-point might be suitable for smaller, less complex integrations, API-led connectivity is the preferred approach for larger organizations looking to build a robust, scalable integration ecosystem.
See also: Debug Logs in Salesforce
21. How do you manage the governance and lifecycle of APIs within a large enterprise environment?
Managing the governance and lifecycle of APIs in a large enterprise is critical to ensuring consistency, security, and efficiency across the organization. My approach begins with establishing clear API governance policies that define standards for API design, development, and documentation. These policies include naming conventions, versioning strategies, and security protocols that every API must adhere to. By enforcing these standards, I can ensure that APIs are consistent and easy to understand across different teams and projects.
Additionally, I implement a centralized API management platform, such as Mulesoft’s Anypoint Platform, to monitor and control API usage across the enterprise. This platform allows me to manage API access, enforce rate limits, and track usage analytics. It also provides tools for versioning and deprecating APIs, ensuring that older versions are phased out in a controlled manner without disrupting existing integrations. Regular audits and reviews of API usage help me identify areas for improvement and ensure that APIs continue to meet business needs. By combining strong governance with effective lifecycle management, I can ensure that our APIs remain secure, scalable, and aligned with the organization’s goals.
22. Describe your experience with multi-cloud integrations and how you ensure data consistency and security across different cloud platforms.
In today’s increasingly multi-cloud world, I’ve had extensive experience designing and implementing integrations that span multiple cloud platforms, such as Salesforce, AWS, and Azure. One of the key challenges in multi-cloud integrations is ensuring data consistency across these disparate systems. To address this, I typically rely on a centralized data orchestration layer, often implemented using an iPaaS solution like Dell Boomi or Mulesoft. This layer acts as a hub for data transformation, mapping, and synchronization, ensuring that data flows consistently between cloud platforms without any loss or duplication.
Security is another critical concern in multi-cloud integrations. To protect sensitive data as it moves between cloud environments, I enforce strong encryption protocols both in transit and at rest. I also use OAuth 2.0 for secure API authentication and authorization, ensuring that only authorized systems and users can access the data. Additionally, I implement role-based access controls and ensure that each cloud platform adheres to the principle of least privilege. Regular security audits and compliance checks help me stay ahead of potential vulnerabilities, ensuring that the integration meets the highest standards of data protection across all cloud platforms involved.
See also: LWC Interview Questions for 5 years experience
23. How do you design a disaster recovery plan for Salesforce integrations, ensuring minimal downtime and data loss?
Designing a disaster recovery plan for Salesforce integrations is a crucial aspect of maintaining business continuity, especially when dealing with mission-critical data and processes. My approach begins with identifying the potential risks and failure points in the integration architecture, such as data loss, API failures, or middleware outages. Once these risks are identified, I develop a comprehensive recovery strategy that includes data backup and redundancy measures. For instance, I schedule regular data exports from Salesforce to a secure external storage, ensuring that we have up-to-date copies of critical data that can be restored quickly in the event of a failure.
In addition to data backup, I implement failover mechanisms within the integration platform. This might involve setting up redundant middleware instances or using load balancers to automatically redirect traffic to a backup system if the primary system goes down. I also define clear recovery time objectives (RTO) and recovery point objectives (RPO) to ensure that the downtime and data loss are kept to a minimum. Regular disaster recovery drills and testing are essential to validate the effectiveness of the plan and to make necessary adjustments based on evolving business needs and technological changes. By taking these steps, I can ensure that our Salesforce integrations are resilient and that the organization can quickly recover from any disruptions.
24. Explain your approach to integrating Salesforce with legacy systems that have limited API support.
Integrating Salesforce with legacy systems that lack modern API support can be challenging, but it’s a task I’ve tackled successfully through various approaches. One of the primary strategies I use is leveraging middleware platforms like Mulesoft or Dell Boomi, which offer tools to create custom connectors that can interface with legacy systems via more traditional methods, such as database connections, flat files, or even proprietary protocols. By using middleware, I can abstract the complexity of the legacy system and expose its data and functionality as modern APIs, which Salesforce can easily consume.
In cases where middleware isn’t sufficient, I may need to develop custom solutions, such as writing batch scripts or using ETL tools to extract data from the legacy system, transform it as needed, and then load it into Salesforce. I also consider using Salesforce Connect, which allows me to access external data in real-time without the need to store it in Salesforce, effectively creating a virtual integration layer. Throughout this process, data validation and error handling are critical to ensure that the integration is reliable and that data integrity is maintained. By carefully planning and leveraging the right tools, I can successfully bridge the gap between Salesforce and older, less flexible systems.
See also: Salesforce Developer Interview Questions for 8 years Experience
25. How do you ensure compliance with data protection regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA in your Salesforce integrations?
Ensuring compliance with data protection regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA is paramount in any Salesforce integration project I undertake. My first step is to thoroughly understand the specific regulatory requirements that apply to the organization and the data being handled. For example, GDPR requires that personal data be processed in a way that ensures its security, while HIPAA mandates strict controls over healthcare data. With these requirements in mind, I design integrations that enforce data minimization, ensuring that only the necessary data is collected and processed.
Encryption is a key tool in my compliance strategy. I ensure that sensitive data is encrypted both in transit and at rest using industry-standard encryption protocols. Additionally, I implement strong access controls, such as role-based access, to ensure that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive data. For auditing purposes, I enable detailed logging of all data access and processing activities, which can be crucial for demonstrating compliance during audits or in the event of a data breach. Regular training for the team on data protection best practices and keeping up with the latest regulatory updates is also essential to maintaining compliance. By taking these proactive measures, I can ensure that our Salesforce integrations not only function effectively but also adhere to the highest standards of data protection.
Master Salesforce in Hyderabad: Elevate Your Career with Key Skills and Opportunities
Salesforce is rapidly gaining recognition as a critical skill for professionals, especially in tech-driven cities like Hyderabad. As one of India’s leading IT hubs, Hyderabad is home to a diverse range of software companies that heavily rely on Salesforce for customer relationship management (CRM) and other essential business functions. Pursuing a Salesforce training course, particularly in areas such as Salesforce Admin, Developer (Apex), Lightning, and Integration, can significantly enhance your career prospects in Hyderabad. Top companies like Deloitte, Accenture, Infosys, TCS, and Wipro are continually seeking certified Salesforce professionals. The demand for these skills is high, and the associated salaries are very competitive. To capitalize on these career opportunities, it is crucial to select a reputable Salesforce training institute. CRS Info Solutions stands out as a leading Salesforce training institute in Hyderabad, offering specialized courses in Admin, Developer, Integration, and Lightning Web Components (LWC), guiding you towards certification and a successful career in Salesforce.
See also: Salesforce Apex Interview Questions
Why Learning Salesforce is Essential in Hyderabad
Hyderabad has firmly established itself as a major IT hub in India, drawing in multinational corporations and driving a growing demand for skilled professionals. Salesforce, as a top CRM platform, plays a pivotal role in meeting this demand. Salesforce training in Hyderabad provides considerable advantages due to the city’s vibrant job market. Leading software companies such as Deloitte, Accenture, Infosys, TCS, and Wipro are consistently on the lookout for certified professionals who have completed Salesforce courses. These companies require specialists in Salesforce modules like Admin, Developer (Apex), Lightning, and Integration to effectively manage and optimize their Salesforce systems.
Certified Salesforce professionals in Hyderabad not only experience high demand but also enjoy some of the most competitive salaries within the tech industry. This makes learning Salesforce an incredibly valuable career move, offering opportunities for significant career growth and financial rewards. In a competitive job market, earning Salesforce certification from a well-regarded Salesforce training institute can greatly enhance your employability and career opportunities.
Checkout: Variables in Salesforce Apex
Why Choose CRS Info Solutions in Hyderabad
To fully leverage the abundant career opportunities in Hyderabad, it is essential to undergo Salesforce training at a respected and experienced institute. CRS Info Solutions is recognized as one of the top Salesforce training institutes in Hyderabad. The institute offers a comprehensive range of Salesforce courses that cover all critical modules, including Admin, Developer, Integration, and Lightning Web Components (LWC). With a team of expert instructors, CRS Info Solutions ensures that students gain both the theoretical knowledge and practical, hands-on experience necessary to excel in real-world situations.
CRS Info Solutions is committed to helping you achieve Salesforce certification and embark on a successful career within the Salesforce ecosystem. The institute’s focus on practical learning, combined with a thorough and well-rounded curriculum, equips you to meet the expectations of top employers in Hyderabad. With CRS Info Solutions, you can become a certified Salesforce professional, ready to take on impactful roles at companies like Deloitte, Accenture, Infosys, TCS, and Wipro. Considering the lucrative salaries and increasing demand for Salesforce expertise in Hyderabad, choosing CRS Info Solutions for your Salesforce training is a key step towards a successful and fulfilling career in the Salesforce industry

