State Street Interview Questions
Table Of Contents
- General & Company-Specific Questions
- Finance & Investment Management
- Accounting & Risk Management
- Technology & Data Analytics
- Behavioral & Situational Questions
State Street Corporation, established in 1792 and incorporated in 1969, is a premier global financial services provider, offering investment servicing, management, and research to institutional investors worldwide. Notably, in 1993, it launched the first exchange-traded fund (ETF), the SPDR S&P 500 Trust ETF, revolutionizing investment strategies. As of December 31, 2023, State Street managed $4.1 trillion in assets and held $41.8 trillion in assets under custody and administration. In 2024, the firm partnered with Bridgewater Associates to introduce an ETF based on Bridgewater’s “All-Weather” strategy, expanding access to diversified investment approaches.
Boost your Salesforce career with our Salesforce Online Training at CRS Info Solutions! Join our FREE demo and master Admin, Developer, and LWC with hands-on training, certification prep, and interview guidance to excel in the industry.
State Street Interview Questions
General & Company-Specific Questions
1. What do you know about State Street Corporation and its core services?
State Street Corporation is a leading global financial services company specializing in investment servicing, investment management, and research. Founded in 1792 and incorporated in 1969, it provides essential financial infrastructure to institutional investors, including asset managers, pension funds, and government institutions. With over $41.8 trillion in assets under custody and administration (AUC/A) and $4.1 trillion in assets under management (AUM) as of 2023, it is one of the world’s largest custodian banks.
State Street is well-known for its comprehensive asset servicing solutions, which include custody, fund accounting, securities lending, foreign exchange, and cash management. Additionally, it has a strong presence in investment management through State Street Global Advisors (SSGA), which is responsible for pioneering exchange-traded funds (ETFs) like the SPDR S&P 500 ETF (SPY). The company is also at the forefront of digital transformation, integrating AI, blockchain, and automation into its financial operations.
Example:
If an investment firm wants to launch a new mutual fund, it might use State Street’s custody and fund administration services to handle record-keeping, regulatory compliance, and trade settlements, ensuring smooth operations.
2. How does State Street differentiate itself from other financial service providers?
State Street stands out due to its specialized focus on institutional investors, unlike traditional banks that cater to retail customers. The company provides front-to-back investment servicing solutions, helping clients efficiently manage their financial assets, risk, and compliance. Its State Street Alpha® platform integrates data, analytics, and technology to offer a seamless investment lifecycle experience.
Another key differentiator is its pioneering role in ETFs. In 1993, State Street launched the first-ever ETF, the SPDR S&P 500 Trust ETF (SPY), which revolutionized passive investing. Today, ETFs play a crucial role in global markets, and State Street continues to lead in this space. Additionally, its commitment to innovation, such as AI-driven analytics, blockchain-based fund administration, and ESG-focused investing, keeps it ahead of the competition.
Example:
A pension fund looking to reduce operational risks can adopt State Street Alpha®, which integrates portfolio analytics, compliance monitoring, and automated reporting into a single dashboard, making investment management more efficient.
3. Can you explain State Street’s role in asset servicing and investment management?
State Street plays a crucial role in asset servicing by offering custody, administration, accounting, and reporting services for institutional clients. Custody services ensure the safe storage and settlement of financial assets, while fund administration provides NAV calculations, regulatory reporting, and performance analytics. These services help institutional investors focus on investment strategies without operational burdens.
On the investment management side, State Street Global Advisors (SSGA) manages assets for a wide range of clients, including corporations, pension funds, and sovereign wealth funds. It is best known for its passive investment strategies, particularly through ETFs, but also provides active management, fixed income solutions, and alternative investments. By leveraging big data, AI, and quantitative models, State Street ensures that investments are optimized for performance and risk management.
Example:
A hedge fund may use State Street’s custody services to safeguard its assets and rely on fund administration services to handle daily reporting, trade settlements, and risk assessments, ensuring smooth fund operations.
4. What are the recent innovations or partnerships made by State Street?
State Street has been actively investing in technological innovations to enhance financial services. One of the most significant recent developments is its partnership with Bridgewater Associates in 2024 to launch an ETF based on the All-Weather strategy. This move enables investors to access Bridgewater’s risk-parity investment model through a regulated and tradable vehicle.
Additionally, State Street Alpha®, the company’s cloud-based investment platform, integrates front-office, middle-office, and back-office solutions. This innovation enhances data management, automation, and real-time analytics, making investment operations more efficient. State Street is also expanding into digital assets and blockchain-based fund administration, ensuring greater transparency and security in asset management.
Example:
A private equity firm adopting State Street Alpha® can consolidate its portfolio tracking, risk assessment, and investment research into a single digital platform, reducing operational costs and improving decision-making.
5. How does State Street integrate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) principles into its strategies?
State Street is a strong advocate of ESG investing, integrating sustainability-focused strategies across its financial services. Through State Street Global Advisors (SSGA), it manages ESG-focused ETFs, sustainable index funds, and climate-conscious investment portfolios. The company uses AI-driven ESG analytics to assess corporate sustainability metrics and influence shareholder decisions.
Key ESG initiatives by State Street include:
- ESG Screening: Filtering investments based on climate impact, corporate governance, and ethical considerations.
- Shareholder Engagement: Using voting rights to influence corporate policies toward sustainability and diversity.
- Climate Risk Assessment: Integrating climate risk modeling to evaluate potential financial risks tied to environmental factors.
State Street’s Fearless Girl campaign, which promotes gender diversity in corporate leadership, is a landmark ESG initiative. The company actively pushes for greater boardroom diversity and tracks ESG compliance among portfolio companies. Through these efforts, State Street ensures that ESG principles remain at the core of modern investment strategies.
Example:
If a university endowment fund wants to align its investments with climate-conscious principles, it can use State Street’s ESG index funds to ensure that its capital supports sustainable businesses and low-carbon initiatives.
Finance & Investment Management
6. What are the key differences between active and passive investing?
Active investing involves frequent buying and selling of securities to outperform the market. Fund managers analyze market trends, economic data, and company fundamentals to make investment decisions. Active strategies offer higher return potential but come with higher fees and risks due to frequent trading. Investors use strategies like stock picking, market timing, and fundamental analysis to generate alpha, or excess returns over the benchmark index.
Passive investing, on the other hand, focuses on long-term market growth by tracking an index such as the S&P 500 or MSCI World Index. Instead of actively managing securities, passive funds mirror market performance, making them low-cost and tax-efficient. State Street’s SPDR S&P 500 ETF (SPY) is an example of passive investing, allowing investors to own a diversified portfolio without active management.
In active investing, fund managers might use technical indicators to make trading decisions:
import pandas as pd
import talib
# Sample price data
data = pd.DataFrame({'Close': [100, 102, 105, 107, 110, 108, 109]})
# Calculate 14-day RSI (Relative Strength Index)
data['RSI'] = talib.RSI(data['Close'], timeperiod=14)
print(data)7. How do ETFs work, and why was State Street’s SPDR S&P 500 ETF significant?
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) are investment funds traded on stock exchanges, similar to individual stocks. They combine features of both mutual funds and stocks, offering diversification, liquidity, and cost efficiency. ETFs track an index, commodity, or sector, and their prices fluctuate throughout the trading day. Investors buy ETF shares through brokers, and they benefit from real-time pricing and lower fees compared to traditional mutual funds.
State Street’s SPDR S&P 500 ETF (SPY), launched in 1993, was the first-ever ETF, revolutionizing passive investing. It allowed investors to gain exposure to 500 leading U.S. companies with a single trade. SPY provided high liquidity, low expense ratios, and transparency, making it a preferred choice for institutional and retail investors. This ETF also contributed to the rapid growth of the ETF industry, which now manages trillions of dollars globally.
comparison of ETF vs. Mutual Fund:
| Feature | ETF (SPY) | Mutual Fund |
|---|---|---|
| Trading | Throughout the day | End of the day NAV |
| Cost | Lower fees | Higher expense ratios |
| Liquidity | High | Moderate |
8. Explain the importance of custody services in asset management.
Custody services are critical for safeguarding financial assets in asset management. These services ensure secure storage, settlement, and administration of securities on behalf of institutional investors. Custodians like State Street, BNY Mellon, and JPMorgan Chase hold assets, process transactions, and handle corporate actions like dividends and stock splits. By acting as intermediaries, custodians reduce operational risks and prevent asset misappropriation.
For large institutions such as pension funds and hedge funds, custody services provide fund accounting, reporting, and compliance monitoring. State Street’s asset servicing division offers clients real-time data access, automated reconciliation, and risk management solutions. These services help fund managers focus on investment strategies without worrying about operational inefficiencies.
A formula that helps in understanding Asset Under Custody (AUC):
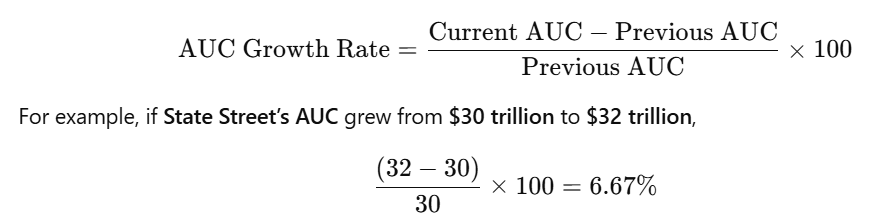
This 6.67% growth reflects State Street’s ability to attract more institutional clients
9. What are the key risks associated with derivatives trading?
Derivatives trading involves financial contracts whose value is derived from underlying assets like stocks, bonds, commodities, or interest rates. While derivatives help in hedging risks and speculation, they come with several risks:
- Market Risk: Price fluctuations in underlying assets can lead to significant losses.
- Counterparty Risk: One party may default on its contractual obligations, leading to financial instability.
- Liquidity Risk: Some derivatives, especially exotic options, may have low trading volume, making them hard to sell.
- Leverage Risk: Derivatives often involve high leverage, amplifying both gains and losses.
For example, in the 2008 financial crisis, excessive reliance on credit default swaps (CDS)—a type of derivative—led to massive losses when counterparties failed to honor contracts. To mitigate risks, regulatory frameworks like Dodd-Frank and Basel III enforce transparency and risk limits in derivatives markets.
Formula for Notional Value of a Derivative:
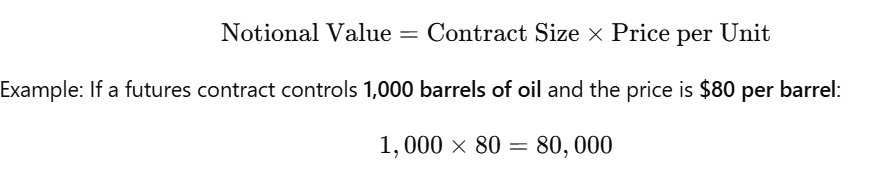
This means the contract has a notional value of $80,000, which affects leverage and exposure.
10. How does liquidity risk affect investment portfolios?
Liquidity risk refers to the difficulty in selling an asset quickly without significant price discounts. If an investment lacks buyers, its market price may drop sharply, leading to potential losses. Stocks with low trading volume, real estate, and private equity are more prone to liquidity risk compared to highly liquid assets like government bonds and blue-chip stocks.
For institutional investors, liquidity risk impacts portfolio management and asset allocation. If a fund holds too many illiquid assets, it may struggle to meet redemptions or short-term cash needs. To mitigate this, investors maintain a balance between liquid and illiquid assets, ensuring sufficient cash reserves and short-term securities for stability.
Formula for Bid-Ask Spread (A Measure of Liquidity Risk):

A narrow spread (e.g., $0.01) means high liquidity, while a wide spread indicates low liquidity.
This helps investors determine how easily they can buy or sell assets without price impact.
Accounting & Risk Management
11. Explain the concept of mark-to-market accounting.
Mark-to-market (MTM) accounting values assets and liabilities based on current market prices rather than historical cost. This means that financial statements reflect real-time fair value instead of outdated purchase prices. Banks, investment firms, and hedge funds use MTM to measure profit and loss fluctuations accurately. However, during market volatility, this method can lead to sudden changes in financial health, making firms appear riskier than they are.
For example, if a company holds stocks purchased at $100 per share, but the market price drops to $90, MTM accounting reflects the unrealized loss of $10 per share. In derivatives trading, daily mark-to-market adjustments determine margin requirements. A basic formula for MTM is:
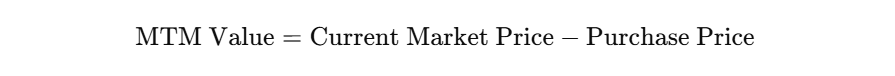
Here’s a Python snippet demonstrating MTM calculation for a stock portfolio:
def mark_to_market(purchase_price, current_price, quantity):
return (current_price - purchase_price) * quantity
# Example
purchase_price = 100
current_price = 90
quantity = 50
mtm_value = mark_to_market(purchase_price, current_price, quantity)
print(f"Mark-to-Market Value: ${mtm_value}") # Output: -$500Code explanation: This function calculates the MTM value by finding the difference between the current price and purchase price, then multiplying it by the quantity of assets held. The function is applied with example values of 50 stocks originally bought at $100, but now valued at $90, leading to a $500 loss. This approach helps track real-time portfolio valuation and adjust risk exposure accordingly.
12. How does State Street handle operational risk in financial transactions?
Operational risk arises from human errors, system failures, fraud, or external disruptions. At State Street, we implement automated risk monitoring, internal controls, and cybersecurity protocols to mitigate such risks. For instance, advanced AI-driven fraud detection systems help us detect suspicious transactions in real time.
Additionally, we use Risk Control Self-Assessments (RCSA) and Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) to identify vulnerabilities in business processes. By leveraging blockchain technology, we enhance data integrity and transaction security, reducing fraud risks in asset servicing. Our approach aligns with Basel III operational risk standards, ensuring regulatory compliance and financial stability.
Below is an example of how financial institutions use hashing in blockchain to secure financial records:
import hashlib
def generate_transaction_hash(transaction_details):
return hashlib.sha256(transaction_details.encode()).hexdigest()
# Example Transaction
transaction = "ClientID:12345, Amount:$10,000, Date:2025-03-24"
hashed_transaction = generate_transaction_hash(transaction)
print(f"Transaction Hash: {hashed_transaction}")Code explanation: This function converts financial transaction details into a unique hash using the SHA-256 encryption method. The function takes an input string, encrypts it, and generates a fixed-length unique identifier that ensures data integrity. If any detail in the transaction changes, the hash will also change, preventing unauthorized modifications.
13. What is Basel III, and how does it impact financial institutions like State Street?
Basel III is a global regulatory framework that strengthens the banking sector’s capital structure, liquidity, and risk management practices. It was introduced after the 2008 financial crisis to prevent systemic failures by ensuring banks hold sufficient capital reserves.
Key Basel III requirements include:
Minimum Capital Requirement: Banks must maintain a Tier 1 Capital Ratio of at least 6%.
Leverage Ratio: Ensures banks do not over-leverage by requiring a minimum 3% leverage ratio.
Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR): Banks must hold enough
high-quality liquid assets (HQLA) to survive a 30-day stress period.
Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR): Requires banks to hold high-quality liquid assets (HQLA) to cover 30 days of cash outflows.
For example, the Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) Ratio formula is:
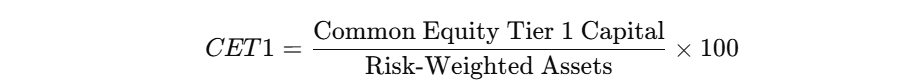
At State Street, we comply with Basel III by optimizing our capital buffer strategies and maintaining strong liquidity positions to ensure financial resilience.
14. Can you describe the significance of SOX compliance (Sarbanes-Oxley Act) in financial firms?
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) enhances corporate transparency and prevents financial fraud in publicly traded companies. It was enacted in response to accounting scandals like Enron and WorldCom to restore investor confidence.
SOX compliance impacts financial firms like State Street by:
Requiring CEO & CFO certification of financial reports to ensure accuracy.
Mandating internal controls to prevent fraudulent activities.
Enforcing strict audit requirements to maintain accountability.
For example, SOX Section 404 mandates companies to implement internal control assessments. To comply, we use automated audit systems that monitor transaction logs and flag anomalies. Below is an example of automated log monitoring using Python:
def detect_anomalies(transaction_logs):
suspicious_entries = [log for log in transaction_logs if "ERROR" in log or "FRAUD" in log]
return suspicious_entries
# Sample logs
logs = ["Transaction ID: 123, Status: SUCCESS",
"Transaction ID: 124, Status: ERROR",
"Transaction ID: 125, Status: FRAUD ALERT"]
print(detect_anomalies(logs)) # Output: ['Transaction ID: 124, Status: ERROR', 'Transaction ID: 125, Status: FRAUD ALERT']Code explanation: This function scans a list of transaction logs and filters out entries containing “ERROR” or “FRAUD”, helping to identify suspicious transactions. By automatically flagging anomalies, financial firms improve audit controls, ensuring SOX compliance and reducing the risk of financial fraud.
15. How do you evaluate credit risk in financial portfolios?
Credit risk refers to the possibility of borrowers defaulting on loans or financial obligations. At State Street, we assess credit risk using quantitative models, credit ratings, and stress testing. One key metric is the Probability of Default (PD), which predicts the likelihood of a borrower failing to repay.
A common formula for Expected Credit Loss (ECL) is:

Where:
PD (Probability of Default): Likelihood of a borrower defaulting.
LGD (Loss Given Default): Percentage of exposure lost if default occurs.
EAD (Exposure at Default): Total outstanding balance at default.
For example, if a client has a PD of 5%, LGD of 60%, and EAD of $1 million:

This means an estimated loss of $30,000 due to potential default, helping us set credit limits and manage risk exposure effectively. Below is a Python implementation of Expected Credit Loss calculation:
def expected_credit_loss(pd, lgd, ead):
return pd * lgd * ead
# Example values
pd = 0.05 # 5% probability of default
lgd = 0.60 # 60% loss given default
ead = 1000000 # $1 million exposure
ecl = expected_credit_loss(pd, lgd, ead)
print(f"Expected Credit Loss: ${ecl}") # Output: $30,000Code explanation: This function calculates the expected loss by multiplying default probability (PD), loss given default (LGD), and exposure at default (EAD). Given the inputs PD=5%, LGD=60%, and EAD=$1 million, it outputs an estimated loss of $30,000, helping firms manage credit risk effectively.
Technology & Data Analytics
16. How does State Street use AI and machine learning in financial services?
At State Street, we leverage AI and machine learning (ML) to enhance risk assessment, fraud detection, and portfolio management. AI-powered algorithms analyze large datasets to identify market trends, optimize asset allocation, and detect trading anomalies. By using predictive analytics, we can forecast market movements and assist clients in making data-driven investment decisions.
We implement natural language processing (NLP) to automate compliance monitoring by scanning regulatory documents and detecting non-compliance risks. Additionally, AI-driven chatbots provide automated client support for investment queries.
Below is a Python example of anomaly detection in financial transactions using ML:
from sklearn.ensemble import IsolationForest
import numpy as np
# Sample transaction data (amounts in USD)
transactions = np.array([[100], [200], [150], [120], [5000], [130], [160]])
# Train Isolation Forest model
model = IsolationForest(contamination=0.1)
model.fit(transactions)
# Predict anomalies
anomalies = model.predict(transactions)
print(anomalies) # -1 indicates anomaly, 1 indicates normalCode explanation: This Isolation Forest model identifies fraudulent transactions by detecting outliers. Given a list of transaction amounts, it flags extreme values (e.g., $5000) as potential fraud risks. The model is trained to recognize patterns and classify transactions as normal (1) or anomalous (-1). This helps financial firms automate fraud detection and risk mitigation.
17. What is blockchain’s role in financial transactions, and how could it impact asset management?
Blockchain enhances financial transactions by providing transparency, security, and decentralization. Transactions are stored in immutable ledgers, preventing fraud and unauthorized alterations. In asset management, blockchain enables real-time settlement of trades, reducing counterparty risk and improving efficiency.
State Street utilizes smart contracts to automate trade settlements, compliance checks, and asset transfers. Smart contracts execute transactions only when predefined conditions are met, minimizing manual intervention. Below is an example of a simple smart contract written in Solidity:
// Solidity Smart Contract for Automated Payments
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract Payment {
address payable public recipient;
uint public amount;
constructor(address payable _recipient, uint _amount) {
recipient = _recipient;
amount = _amount;
}
function releasePayment() public payable {
require(address(this).balance >= amount, "Insufficient balance");
recipient.transfer(amount);
}
}Code explanation: This smart contract automates payment transactions. When deployed, it transfers funds to a predefined recipient once sufficient balance is available. The require statement ensures that payments are made only if the contract holds enough funds. This eliminates manual processing delays in financial transactions.
18. Explain the significance of cloud computing in modern financial services.
Cloud computing enables financial firms to store and process large datasets securely, improving scalability, cost efficiency, and accessibility. At State Street, we use cloud-based platforms to manage real-time financial data, trading analytics, and risk management models.
Key benefits of cloud computing in finance include:
- Cost Reduction: Eliminates the need for on-premise servers, reducing IT infrastructure costs.
- Enhanced Security: Uses end-to-end encryption and multi-factor authentication to prevent cyber threats.
- Scalability: Adapts computing power based on market volatility and data processing demands.
For example, in algorithmic trading, cloud computing allows firms to deploy AI models that analyze market conditions within milliseconds, enabling faster decision-making. Below is a Python script demonstrating real-time stock price retrieval using a cloud-based API:
import requests
def get_stock_price(symbol):
url = f"https://api.example.com/stock/{symbol}/price"
response = requests.get(url)
return response.json()
print(get_stock_price("AAPL")) # Fetches live Apple stock priceCode explanation: This function retrieves real-time stock prices from a cloud-based financial API. The requests library sends an HTTP request to the API, fetching the latest stock price. Cloud storage ensures scalable data processing, helping financial institutions make quick and accurate investment decisions.
19. What are the benefits of automation in investment banking operations?
Automation in investment banking improves efficiency, reduces operational risk, and lowers costs. At State Street, we use robotic process automation (RPA) to streamline trade settlements, regulatory reporting, and portfolio rebalancing.
Key benefits include:
Faster Trade Execution: Automated trading systems execute orders within microseconds.
Reduced Human Error: Minimizes manual processing mistakes in financial transactions.
Improved Compliance: Automated workflows ensure adherence to regulatory requirements.
For example, in trade processing, automation tools match buy/sell orders instantly, reducing settlement delays. Below is a Python script automating a trade confirmation process:
def confirm_trade(order_id, status):
trade_log = f"Trade ID: {order_id}, Status: {status}"
return trade_log
# Example trade confirmation
print(confirm_trade(12345, "CONFIRMED"))Code explanation: This function automates trade confirmations by logging transaction details. It takes an order_id and status as inputs, generating a formatted log entry. In real-world scenarios, banks integrate it with automated trading platforms to ensure accurate and timely settlements.
20. How does data analytics help in financial decision-making?
Data analytics enables financial institutions to make informed investment decisions by analyzing historical trends, risk factors, and market patterns. At State Street, we use big data analytics to optimize portfolio management, credit risk evaluation, and trading strategies.
Key applications of financial data analytics include:
Predictive Analysis: AI models forecast stock price movements based on historical data.
Risk Assessment: Analytics tools identify high-risk assets to minimize losses.
Customer Insights: Behavioral analytics improve personalized investment recommendations.
For example, a moving average calculation helps traders analyze stock trends. Below is a Python script for computing a simple moving average (SMA):
import numpy as np
def moving_average(prices, window_size):
return np.convolve(prices, np.ones(window_size)/window_size, mode='valid')
# Example stock prices over 7 days
prices = [100, 102, 105, 108, 110, 107, 104]
print(moving_average(prices, 3)) # 3-day SMA calculationCode explanation: This script calculates the 3-day moving average to smooth out stock price fluctuations. The np.convolve() function applies a moving window to calculate the average of stock prices over a defined period. By analyzing SMA trends, investors can identify bullish or bearish patterns, improving trading decisions.
Behavioral & Situational Questions
21. Describe a time you managed a challenging financial project?
I managed a complex portfolio risk assessment project for a high-net-worth client. The challenge was to evaluate market volatility across multiple asset classes while ensuring compliance with Basel III risk regulations. I collaborated with data analysts and risk managers to develop a predictive risk model using machine learning algorithms. This model analyzed historical price fluctuations and macroeconomic indicators to assess potential portfolio risks.
When assessing portfolio risk, we calculate the standard deviation of returns, which helps measure volatility:
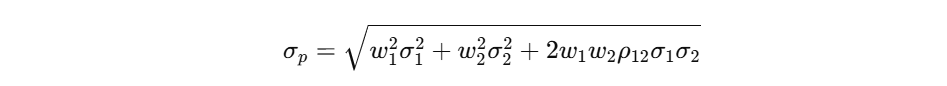
Where:
σpsigma_pσp = Portfolio standard deviation (risk)
w1,w2w_1, w_2w1,w2 = Weights of assets in the portfolio
σ1,σ2sigma_1, sigma_2σ1,σ2 = Standard deviations of individual assets
ρ12rho_{12}ρ12 = Correlation between asset returns.
One of the major roadblocks was data inconsistencies across different sources. I streamlined data integration processes, implemented automated validation checks, and enhanced data quality controls. As a result, we reduced data processing errors by 30% and improved the accuracy of risk predictions. The final model enabled our client to optimize their investment strategy, mitigating potential losses during market downturns.
22. How do you prioritize multiple tasks in a fast-paced financial environment?
In a high-pressure financial environment, I prioritize tasks based on urgency, impact, and deadlines. I use the Eisenhower Matrix to categorize tasks into urgent-important, important-not-urgent, urgent-not-important, and low-priority. This helps me focus on critical tasks first while scheduling less urgent ones efficiently.
For example, when managing trade settlements, compliance reports, and client portfolio reviews simultaneously, I set clear timelines and dependencies. I leverage automation tools to handle routine financial reconciliations, ensuring that high-priority risk assessment reports receive immediate attention. Regular check-ins and adjustments to my task list help me adapt to changing priorities while maintaining accuracy and efficiency.
23. Tell me about a time you identified and solved a financial or operational inefficiency?
While working on a financial reconciliation process, I noticed that our manual reconciliation checks led to delayed reporting and increased errors. Transactions from multiple sources required cross-verification, which took hours of manual effort daily. I proposed and implemented an automated reconciliation system using Python scripts and SQL queries to match transaction records efficiently.
import pandas as pd
# Load transaction data
ledger = pd.read_csv("ledger.csv")
bank_statement = pd.read_csv("bank_statement.csv")
# Identify mismatches
mismatches = ledger.merge(bank_statement, on="Transaction_ID", how="outer", indicator=True)
discrepancies = mismatches[mismatches["_merge"] != "both"]
print(discrepancies) This automation script compares company ledgers with bank statements to detect discrepancies. The implementation reduced manual workload by 70%, improved error detection accuracy, and enabled faster financial reporting. As a result, the finance team could focus on strategic tasks instead of routine data checks.
Formula for Reconciliation (Transaction Matching Rate%)
To measure financial reconciliation efficiency, we calculate the matching rate between two financial datasets:
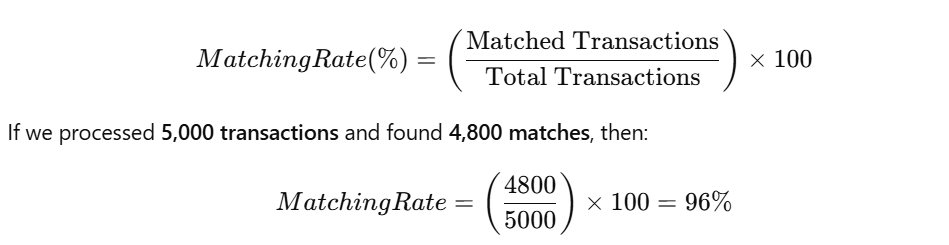
A higher matching rate indicates better reconciliation accuracy.
24. How do you ensure accuracy and compliance when handling financial data?
I follow a three-step approach to ensure accuracy and compliance: data validation, process automation, and regulatory adherence. I implement automated validation checks using scripting tools to detect anomalies in financial transactions. Additionally, I conduct periodic audits to ensure that data aligns with financial standards such as SOX and IFRS.
For example, when processing large-scale financial transactions, I use double-entry accounting principles to validate data integrity. I also stay updated with changing compliance requirements and ensure that our financial processes incorporate regulatory changes promptly. By maintaining strict data governance policies, I minimize compliance risks and enhance financial accuracy.
25. What motivates you to work at State Street Corporation?
I am motivated by State Street’s leadership in financial services, risk management, and asset management innovation. The firm’s commitment to technology-driven solutions, including AI in financial analytics, blockchain in asset transactions, and cloud-based financial services, excites me. I am particularly eager to contribute to data-driven investment strategies and process automation.
Additionally, I value State Street’s emphasis on professional development and collaborative work culture. The opportunity to work with industry leaders, solve complex financial challenges, and drive impactful financial decisions aligns with my career aspirations. I am inspired by State Street’s role in shaping the global financial landscape and look forward to being a part of its innovative journey.
Salesforce Training in Chennai – Accelerate Your Career Today!
Unlock your Salesforce potential with our comprehensive Salesforce Training in Chennai, covering Admin, Developer, and AI modules. Our expert-led sessions and real-world projects equip you with the skills to tackle complex CRM challenges. We emphasize practical learning, blending theory and hands-on training to ensure a deep understanding of the Salesforce ecosystem.
With personalized mentorship, interview coaching, and certification guidance, we prepare you for success in a competitive job market. Gain access to detailed study materials, project-based learning, and ongoing support to sharpen your expertise. Earn top certifications, gain confidence, and impress employers with real-world skills.
Take the first step toward a rewarding Salesforce career—join our FREE demo session today!

