JWT vs. JWT Token Exchange in Named Credentials?

Question:
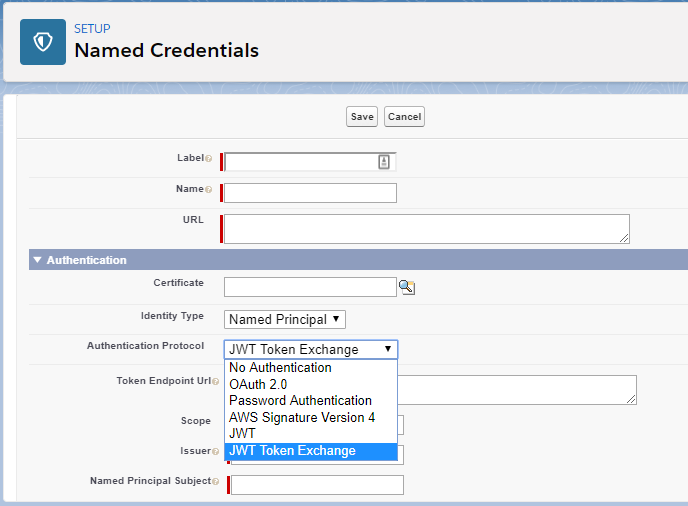
When setting up a Named Credential in Salesforce with the Identity Type set to “Named Principal,” there are two options available under the “Authentication Protocol” dropdown: “JWT” and “JWT Token Exchange.” What is the difference between these two options? Additionally, when “JWT Token Exchange” is selected, two extra fields—”Scope” and “Token Endpoint URL”—appear. Does this mean that the “URL” field at the top of the Named Credential is only for the service endpoint, while the “Token Endpoint URL” is used for obtaining the access token? Does Salesforce assume the service endpoint URL and authentication token endpoint URL are the same when “JWT” is selected instead of “JWT Token Exchange”?
Answer:
The two options, “JWT” and “JWT Token Exchange,” are distinct in how Salesforce handles authentication and token generation for the Named Credential.
CRS Info Solutions in Ahmedabad offers expert-led Salesforce Training in Ahmedabad with hands-on projects—join today for a free demo and boost your skills!!!
Here is an explanation of both:
JWT:
When “JWT” is selected as the Authentication Protocol, Salesforce directly issues a JWT token. When you use the Named Credential in your code to call a third-party service, Salesforce includes the issued JWT token as a bearer token in the request’s Authorization header. This approach is appropriate when the third-party service directly supports JWT as a bearer token for authorization. In this case, the “URL” field in the Named Credential represents the endpoint of the service being called, and no token exchange process is involved.
JWT Token Exchange:
When “JWT Token Exchange” is selected, Salesforce issues a JWT token and sends it to an external authorization service. The authorization service exchanges the provided JWT token for an access token. Salesforce then uses this access token as the bearer token in the request’s Authorization header when calling the third-party service.
The “Token Endpoint URL” specifies the endpoint of the external authorization service used to exchange the JWT token for an access token. The “Scope” field is used to specify the scope of the access token being requested. In this configuration, the “URL” field in the Named Credential is still the endpoint for the third-party service you want to call, while the “Token Endpoint URL” is used specifically for authentication.
Example Scenario for JWT:
If a third-party API directly supports JWT as a bearer token:
Authorization: Bearer <JWT>Code explanation:
The Authorization: Bearer <JWT> header is used to send a JWT (JSON Web Token) as a bearer token in an HTTP request. It authorizes the client to access a resource by including the token in the request’s header, where <JWT> is replaced with the actual encoded token string issued by the authentication provider.
Example Scenario for JWT Token Exchange:
1.Salesforce sends a JWT to the token endpoint:
POST <Token Endpoint URL>
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer
assertion=<JWT>Code explanation:
The above code represents an HTTP POST request sent to the token endpoint URL for exchanging a JWT token for an access token. The request uses the application/x-www-form-urlencoded content type and includes the grant_type parameter specifying the JWT Bearer flow and the assertion parameter containing the encoded JWT.
2.The authorization service responds with an access token:
{
"access_token": "xyz123",
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 3600
}Code explanation:
The JSON response represents the result of a successful token exchange. It includes an access_token (the actual token used for authentication), a token_type (indicating the type of token, e.g., “Bearer”), and expires_in (the token’s validity period in seconds, here 3600 seconds or 1 hour).This access token can then be used in the Authorization header of subsequent HTTP requests to authenticate with the target service.
3.Salesforce uses the returned access token as a bearer token when calling the service:
Authorization: Bearer xyz123Code explanation:
The line Authorization: Bearer xyz123 is an HTTP header used in API requests to include a bearer token (xyz123) for authentication, indicating that the sender is authorized to access the API resource.
Summing Up:
The difference between “JWT” and “JWT Token Exchange” in Salesforce Named Credentials lies in how tokens are handled for authentication. With “JWT,” Salesforce generates a JWT token and sends it directly as a bearer token to the service endpoint. In contrast, “JWT Token Exchange” involves sending a Salesforce-generated JWT to an external authorization service to exchange it for an access token, which is then used for API requests. This distinction allows integration with services requiring either direct JWT authorization or additional token exchange processes.
Accelerate Your Salesforce Career with Training in Ahmedabad
Unlock new career opportunities with Salesforce through expert-led training from CRS Info Solutions in Ahmedabad. Our comprehensive courses cover essential areas like Salesforce Admin, Developer, and AI modules, emphasizing real-time project-based learning to equip you with practical skills. Whether you’re a beginner or looking to enhance your expertise, our industry-focused curriculum ensures you gain the knowledge and confidence needed to thrive in the Salesforce ecosystem. Led by experienced professionals, our program prepares you for real-world challenges and helps you become job-ready.
Our training offers hands-on learning, personalized mentorship Salesforce Training in Ahmedabad , and resources like detailed class notes, certification guidance, and interview preparation to help you succeed. With a focus on practical application and expert support, you’ll be fully equipped to step into your next Salesforce role.
Don’t miss the chance to advance your career—enroll today and join our free demo session to start your Salesforce journey!!!

